Impact of Large Carnivores across Europe
Predation on livestock and other domestic animals and damage to agriculture is the main source of conflicts caused by large carnivores in Europe and the main cause of their persecution in the past and today. In addition, bears can occasionally attack and kill humans, and fear of wolves is still widespread even though no lethal attack has been verified in Europe for more than 40 years (see our facts and common misconceptions page). Damages to livestock have economic impacts for livestock breeders but they also have broader impacts such as emotional effects coming on top of the many other pressures on extensive grazing systems.
Ten case studies areas have been chosen to represent the variety of impacts of large carnivores across the EU. Focusing on scales lower than the national level, the studies reveal details of the carnivores-human conflicts that often are not evident from national statistics. Local geographies and socio-economic conditions play a critical role in shaping values, attitudes and behaviour of local communities toward carnivores. Analysing existing data, supplemented by expert and / or stakeholder interviews, the cases demonstrate the range of possible impacts across the European territory. Livestock depredation and the availability, uptake and effectiveness of protection measures is a theme for all cases. Several cases also examine the impacts of bears and their interactions with human activity.

Download the reports here:
- Slovenia. Balancing conservation and coexistence with brown bears.
- Szeklerland, Romania. The impact of brown bears and the ways of coexistence.
- Trentino, Italy. Bear attacks on humans.
- Saxony, Germany. Insight into a wolf–livestock conflict 25 years after wolf recolonization.
- Northern Finland. Large carnivores in the reindeer husbandry area.
- Austria. Wolves and livestock in diverse landscapes – from the Pannonian Basin to the Alps.
- Province of Ávila, Spain. Wolf and extensive cattle interactions.
- Vercors Regional Natural Park, France. The wolf, extensive livestock and use of protection measures.
- Ioannina Regional Unit, Greece. Wolf and extensive sheep/goat and cattle interactions.
- The Province of Grosseto, Italy. Wolf impact on small scale extensive livestock.
Large carnivore livestock damages
Data on depredation of livestock is not easily comparable across the EU. There is no one system for collecting incidents used in all countries and the reliability of reporting depends on the compensation system in place.
Ideally in order to be able to say something about the causes of depredation, data should be available on a regional level and comparable across years. The EU Large Carnivore Platform is continuing a system of data collection put in place by the LIFE EUROLARGECARNIVORES Project to collect individual case-based data in a comparable way across the EU.
Results from the analysis are reported in detail in Livestock depredation and large carnivores in Europe: Overview for the EU Platform and through a range of supporting qualitative best practices gathering information from different member states and regions: National and regional case studies on livestock depredation and large carnivores.

Initial Results
The following main findings emerge from the report:
- First analysis indicates that while depredation increases with the geographical spread of the wolf to new areas, it does not necessarily increase with increased wolf numbers in one specific area. The relationship is complex and depends particularly on the availability of natural prey, landscape, and the use of protection measures.
- Overall the trend is, after an initial increase, for a decrease in incidents potentially linked to protection measures being put in place.
- Although their diet can vary, wolves are natural hunters of wild ungulates, but they also have a tendency to attack unprotected livestock. Extensively grazing sheep were the livestock species affected most frequently (over 50% of all incidents), followed by cattle and goats.
- Incident density and number of animals killed showed significant variation across the EU countries and within countries between regions.
Mapping livestock damages
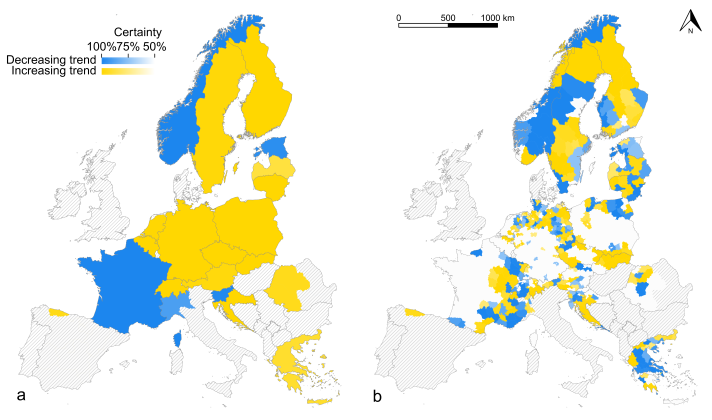
Data is also presented in the form of maps for different administrative levels. This map is showing damage trends, taking into consideration the change in depredation incidents and some other factors over a four-year period.
Wolf-caused livestock damage trends (2018-21) at the country level (a) and NUTS3 level (b)
Preventing livestock damages
In most EU Member States funding is available to help livestock keepers protect their stock against attacks by wolves and bears. Measures to protect livestock include fencing, livestock guarding dogs and shepherding.
Best practice examples documenting how coexistence between people and large carnivores can be supported in different countries can be found here.